Syntax
hPatch = swplot.circle(r0, n, R)
hPatch = swplot.circle(r0, n, R, nPatch)
hPatch = swplot.circle(handle, ...)
Description
hPatch = swplot.circle(r0, n, R) creates a triangulated patch of a
surface of a circle in 3D, defined by the center position, normal vector
and radius.
hPatch = swplot.circle(handle, ...) adds the patch object to a given axis
if handle is an axis handle or adds the arrow to an existing
patch object, if the given handle points to a patch object.
Examples
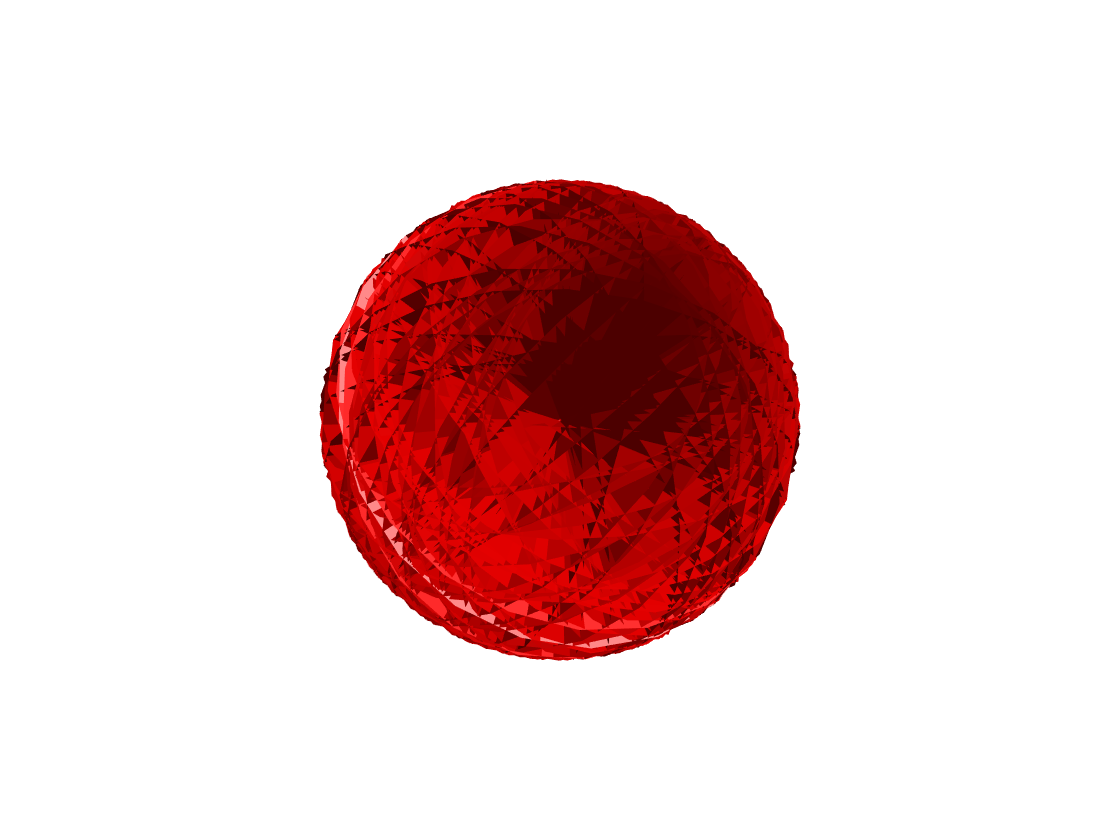
Draw 100 random unit circle surfaces with center at \((0,0,0)\) and random normal vector.
swplot.figure
N = 100
swplot.circle(zeros(3,N),2*rand(3,N)-1,1)
swplot.zoom(30)%
Input Arguments
handle- Handle of an axis or triangulated patch object. In case of patch object, the constructed faces will be added to the existing object.
r0- Center position of the circle in a column vector. Multiple circles can be defined using a matrix with dimensions of \([3\times n_{obj}]\) where each column defines a circle center.
n- Column vector with 3 elements, normal to the circle surface. Multiple
circles can be defined using a matrix with the same dimensions as
r0parameter. R- Radius of the circle, scalar or row vector with \(n_{obj}\) number of elements.
nPatch- Number of points on the circle circumference, default value is stored in
swpref.getpref('npatch'). The generated patch will contain \(n_{patch}\) number of faces and vertices.