Antiferromagnetic nearest-neighbour spin chain
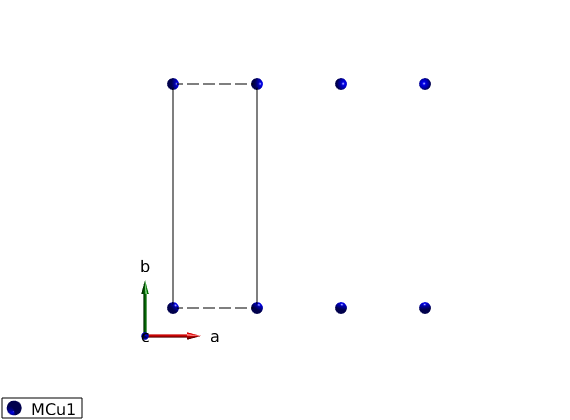
Definition of crystal structure, shortest bonds along the a-axis magnetic Cu+ atoms with S=1 spin.
Contents
Define the lattice
AFMchain = spinw; AFMchain.genlattice('lat_const',[3 8 8],'angled',[90 90 90],'spgr',0); AFMchain.addatom('r',[0 0 0],'S',1,'label','MCu1','color','blue'); disp('Magnetic lattice:') AFMchain.table('matom') plot(AFMchain,'range',[3 1 1])
Magnetic lattice:
ans =
1×4 table
matom idx S pos
______ ___ _ ___________
'MCu1' 1 1 0 0 0
Create antiferromagnetic interactions
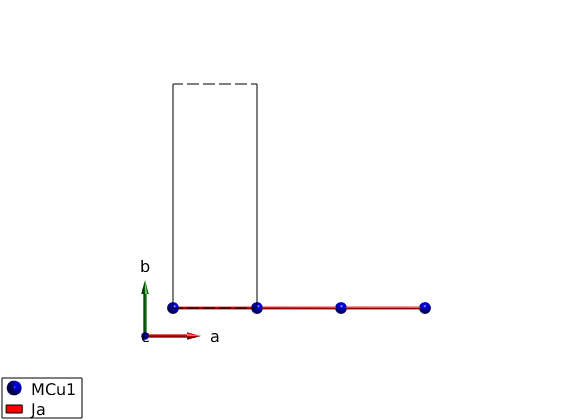
Ja = 1 meV, positive sign denotes antiferromagnetic interaction.
AFMchain.gencoupling('maxDistance',7) AFMchain.table('bond',[1 2]) AFMchain.addmatrix('label','Ja','value',1,'color','red'); AFMchain.addcoupling('mat','Ja','bond',1); disp('After assigning a matrix to a bond:') AFMchain.table('bond',[1 2]) plot(AFMchain,'range',[3 0.9 0.9])
ans =
2×10 table
idx subidx dl dr length matom1 idx1 matom2 idx2 matrix
___ ______ ___________ ___________ ______ ______ ____ ______ ____ ______________
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 3 'MCu1' 1 'MCu1' 1 '' '' ''
2 1 2 0 0 2 0 0 6 'MCu1' 1 'MCu1' 1 '' '' ''
After assigning a matrix to a bond:
ans =
2×10 table
idx subidx dl dr length matom1 idx1 matom2 idx2 matrix
___ ______ ___________ ___________ ______ ______ ____ ______ ____ ________________
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 3 'MCu1' 1 'MCu1' 1 'Ja' '' ''
2 1 2 0 0 2 0 0 6 'MCu1' 1 'MCu1' 1 '' '' ''
Two ways of defining the magnetic structure
Define all spins
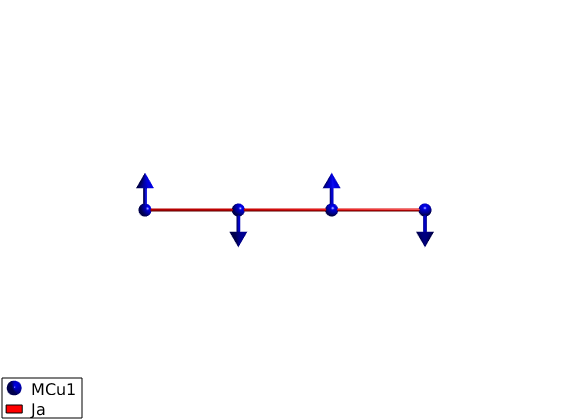
We define a magnetic supercell 2x1x1 of the crystal cell and define both spin direction in the supercell with the following parameters:
- magnetic ordering wave vector k = (1/2 0 0)
- spins pointing along +/- y direction: S = [[0 1 0]' [0 -1 0]']
- normal to the spin vectors n = (1 0 0)
AFMchain.genmagstr('mode','direct','k',[1/2 0 0],'n',[1 0 0],'S',[0 0; 1 -1;0 0],'nExt',[2 1 1]);
Define only one spin
We define the spin direction in the crystallographic unit cell and let the sw.genmagstr() function generate the other spin based on the magnetic ordering wave vector and normal vectors. This method is usefull for creating complex structures. Both methods gives the same magnetic structure, all stored values in the afchain.mag_str field are the same.
AFMchain.genmagstr('mode','helical','k',[1/2 0 0],'n',[1 0 0],'S',[0; 1; 0],'nExt',[2 1 1]); disp('Magnetic structure:') AFMchain.table('mag') % Ground state energy AFMchain.energy plot(AFMchain,'range',[3 0.9 0.9],'cellMode','none','baseMode','none')
Magnetic structure:
ans =
2×8 table
num matom idx S realFhat imagFhat pos kvect
___ ______ ___ _ _____________ _____________ ___________ _________________
1 'MCu1' 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0.5 0 0
2 'MCu1' 1 1 0 -1 0 0 0 -1 1 0 0 0.5 0 0
Ground state energy: -1.000 meV/spin.
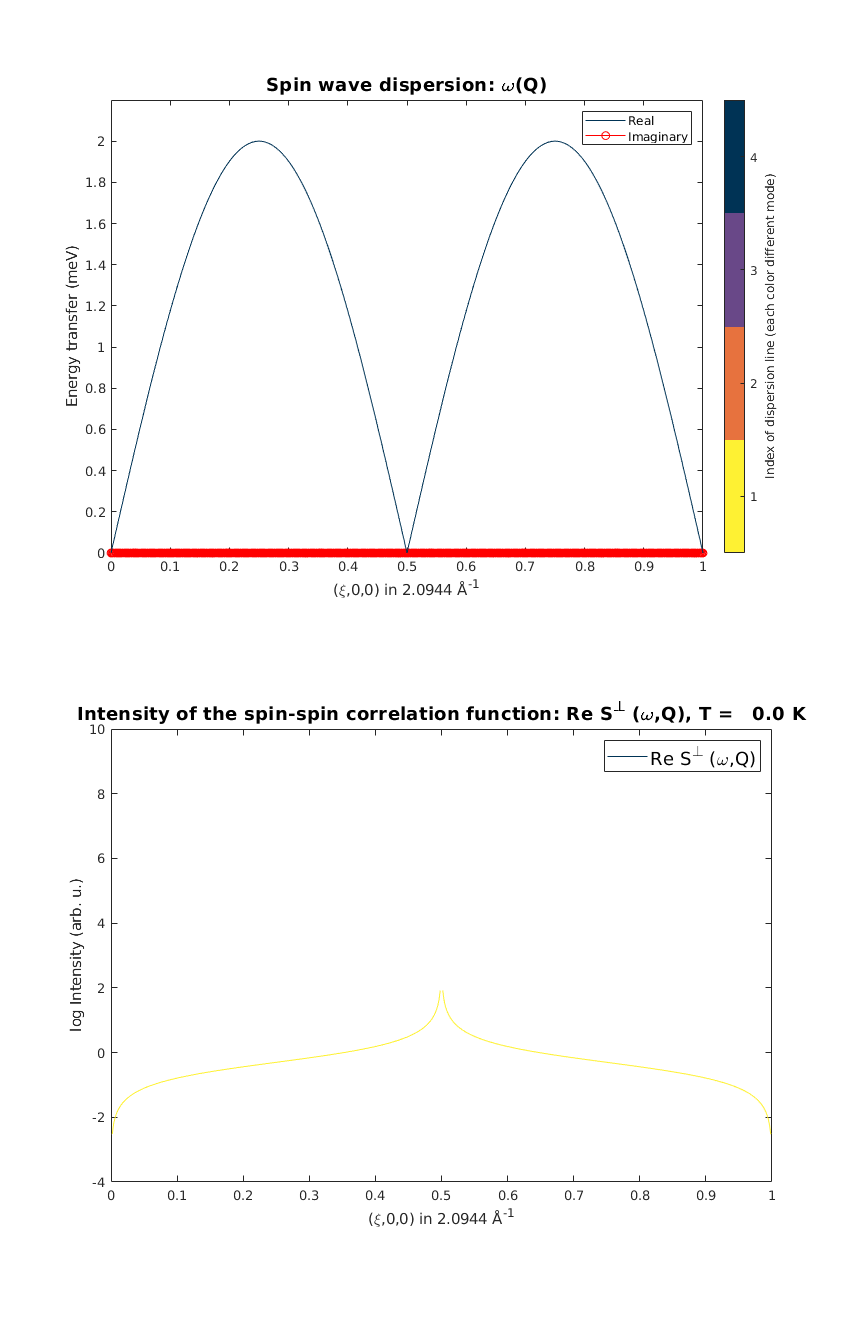
Spin wave spectrum
We calculate the spin wave spectrum and neutron scattering cross sections along the chain direction. The neutron scattering cross section is plotted together with the dispersion (black line).
afcSpec = AFMchain.spinwave({[0 0 0] [1 0 0] 523}, 'hermit',true);
figure
subplot(2,1,1)
sw_plotspec(afcSpec,'mode',4,'dE',0.2,'axLim',[0 3])
% To calculate the intensity, we need to sum up the intensity of the two
% degenerate spin wave mode using the sw_omegasum() function. We plot the
% logarithm of the intensity.
afcSpec = sw_neutron(afcSpec);
afcSpec = sw_egrid(afcSpec,'Evect',linspace(0,6.5,500),'component','Sperp');
afcSpec = sw_omegasum(afcSpec,'zeroint',1e-6);
subplot(2,1,2)
sw_plotspec(afcSpec,'mode',2,'log',true,'axLim',[-4 10])
% Position the figure on the screen, similarly how subplot() positions the
% axes on the figure.
swplot.subfigure(1,3,1)
Written by Bjorn Fak & Sandor Toth 06-Jun-2014, 06-Feb-2015