k=0 Kagome antiferromagnet with DM interaction
We create the lattice with 'P -3' space group and magnetic Cu+ with S=1 spin.
Contents
Define the lattice
DMkag = spinw; DMkag.genlattice('lat_const',[6 6 40],'angled',[90 90 120],'spgr','P -3') DMkag.addatom('r', [1/2 0 0],'S',1,'label', 'Cu1', 'color','r') plot(DMkag,'range',[2 2 1]) swplot.zoom(4)
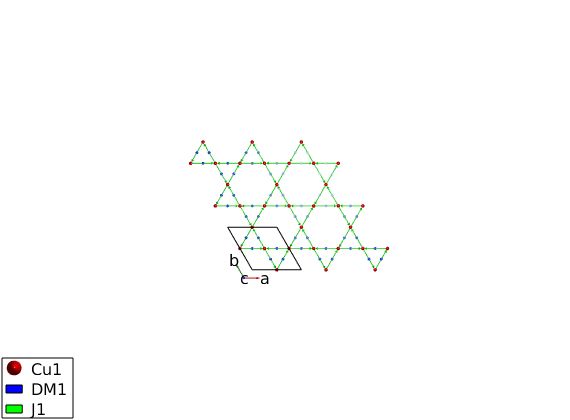
Create bonds and Hamiltonian
Generate the list of bonds and assign a Heisenberg exchange and weak Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction to the fisrt neighbor bonds. The DM interaction vector can be easily created using the spinw.setmatrix function. The corresponding spinw.getmatrix method determines the symmetry allowed components of the DM vector. On the structure plot, the DM interaction vector is symbolized by a vector in the middle of the bond, pointing in the direction of the DM vector. Also important that the bonds are directional, that is shown by the arrows pointing from one atom to another. If one changes the direction of a bond, the corresponding DM vector has to be flipped as well.
DMkag.gencoupling('maxDistance',7) DMkag.addmatrix('label','DM1','value',1,'color','b') DMkag.addmatrix('label','J1','value',1,'color','g') DMkag.addcoupling('mat','DM1','bond',1) DMkag.addcoupling('mat','J1','bond',1) DMkag.setmatrix('mat','DM1','pref',{[0 0 -0.08]}); plot(DMkag,'range',[3 3 1/2]) swplot.zoom(1.2) DMkag.table('mat')
ans =
2×6 table
matrix Mx My Mz type assigned
______ ___________________ ____________________ ___________ _______________ ________
'DM1' 0 -0.08 0 0.08 0 0 0 0 0 'antisymmetric' 'bond'
'J1' 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 'Heisenberg' 'bond'
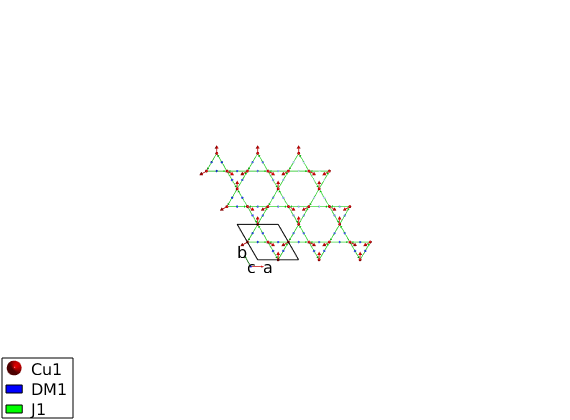
Generate magnetic structure
We create a k = (0 0 0) magnetic structure, with the three spin directions in the unit cell (120 degree between neighbors). The spin vector components are given in the coordinate system of the lattice vectors (abc) and spinw.genmagstr normalizes the moment length to the previously given spin quantum number in the spinw.addatom method.
S0 = [1 -2 1; 2 -1 -1; 0 0 0]; DMkag.genmagstr('mode','direct','k',[0 0 0],'n',[0 0 1],'unit','lu', 'S',S0); DMkag.energy plot(DMkag,'range',[3 3 1/2])
Ground state energy: -1.139 meV/spin.
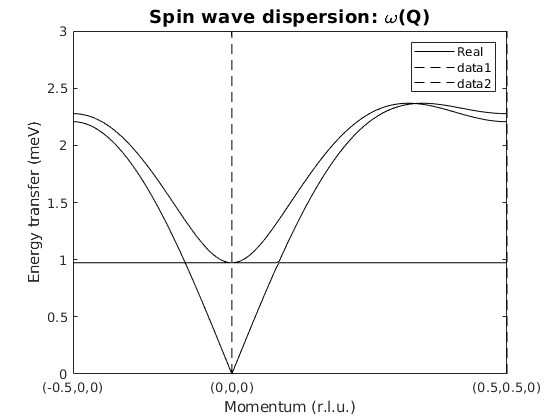
Calculate spin wave dispersion
Qlist = {[-1/2 0 0] [0 0 0] [1/2 1/2 0] 100};
dmkSpec = DMkag.spinwave(Qlist,'hermit',false);
figure
sw_plotspec(dmkSpec,'mode',1,'axLim',[0 3],'colorbar',false,...
'colormap',[0 0 0],'dashed',true)
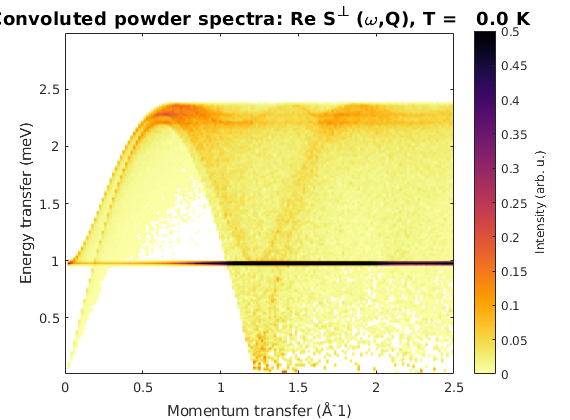
Powder spectrum
The flat mode that is the zero energy mode lifted by the DM interaction is well visible on the powder spectrum.
dmkPow = DMkag.powspec(linspace(0,2.5,150),'Evect',linspace(0,3,250),... 'nRand',1e3,'hermit',false,'imagChk',false); figure sw_plotspec(dmkPow,'axLim',[0 0.5],'dE',0.02)
Written by Bjorn Fak & Sandor Toth 06-Jun-2014, 06-Feb-2017